|
10/27/2022 0 Comments Get Quality Preparation with SAS Platform Administrator (A00-250) CertificationSAS Platform Administrator certification questions and exam summary helps you to get focused on the exam. This guide also helps you to be on A00-250 exam track to get certified with good score in the final exam. SAS Platform Administrator (A00-250) Certification Summary
SAS Platform Administrator (A00-250) Certification Exam Syllabus Managing the SAS Environment [15%] - Secure a SAS platform configuration. - Use operating system controls to protect the SAS configuration directory. - Update SAS Software - Regularly manage and apply hot fixes. - Apply SAS maintenance packs. - Perform SAS license updates. - Work with the SAS Metadata Server. - Configure the initial metadata server to use the network location for backups and the service login account. - Configure the SAS Metadata Server cluster - Install and configure additional metadata server nodes - Manage metadata repositories - Initial authentication to the metadata server - Explain the importance of journaling - Promote metadata and associated content. Monitoring, Logging, and Troubleshooting SAS Servers [15%] - Monitor SAS servers. - Monitor workspace servers and stored process servers. - Use the SAS Environment Manager to view server resources. - Set alerting and escalation functionality - Administer SAS server logging and modify logging configurations. - Change logging levels and locate logs. - Enable trace logging. - Explain the difference between default logging and customized logging. - Utilize dynamic logging. - Troubleshoot basic SAS server issues such as server availability. - Utilize alerts for monitoring - Identify the properties and functionality of SAS servers. - Identify startup order of SAS servers. - Explain the functionality of the object spawner. - Use the Server Manager plug-in to monitor SAS servers. - Use Environment Manager to evaluate the resources available on the SAS servers. Backing Up the SAS Environment [8%] - Backup and restore the SAS environment. - View backup and recovery history. - Run an immediate (ad hoc) backup. - Customize backups. - View information about backup and recovery sources. - View and modify the backup schedule. - Perform full or partial recovery from one of the backups. - Determine when to specify a central vault location. - Explain the limitations of the Deployment Backup and Recovery tool. - Use the SAS Backup Manager in Environment Manager to perform backups. - Use the Roll forward option with metadata backups. - Explain the role of the Deployment agent in the backup. - Use scripts and system utilities to backup metadata - Backup and restore Metadata. - Run an immediate (ad hoc) backup. - Recover the metadata. - Use the backup facility in SAS Management Console. - Configure the backup properties. - View and modify the backup schedule. - Reorganize properties. Administering Users [22%] - Manage connection profiles. - Register users and groups in the metadata. Manage administrative access to the metadata. Manage roles Manage internal SAS accounts - Determine when to store passwords in the metadata - Give users access to processing servers and data servers - Identify SAS server authentication mechanisms. Administering Data Access [20%] - Register libraries and tables in the metadata. - Update table metadata. - Pre-assign a library. - Troubleshoot data access problems. - Use the metadata LIBNAME engine. Managing Metadata Authorization [20%] - Identify how the metadata authorization layer interacts with other security layers. - Identify where, how, and to whom metadata permissions are assigned. - Determine the outcome of metadata authorization decisions. - Use metadata permissions to secure metadata - Use the metadata folder structure to manage access to metadata. - Create and use Access Control Templates. SAS Platform Administrator (A00-250) Certification Questions 01. By default, which groups have WriteMetadata on the Foundation repository? a) PUBLIC b) SASUSERS c) ADMINISTRATORS ONLY d) SAS SYSTEM SERVICES ONLY 02. Every SAS platform implementation includes: a) a foundation repository and a repository manager. b) a foundation repository and a custom repository. c) a custom repository and a repository manager. d) multiple project repositories. 03. Which procedure allows a platform administrator to update table metadata? a) METAUPDATE_RULE b) METASELECT c) METATABLE d) METALIB 04. Given the following authorization settings for Library Sales2: - Library Sales2's parent folder has an explicit grant of RM for Mary. - Library Sales2 has an explicit denial of RM for PUBLIC. Which statement is true? a) Mary can see Library Sales2. b) Mary can see data flagged as PUBLIC in Library Sales2. c) Mary cannot see Library Sales2. d) Mary can see Library Sales2, but not any data flagged as PUBLIC. 05. The SAS Web Infrastructure Platform Data Serverstores content collected by the SAS Environment Agent in what format? a) Gemfire b) SAS Data Sets c) PostgreSQL d) SAS Log 06. Which statement is FALSE regarding the WriteMemberMetadata (WMM) permission? a) WMM is inherited from one folder to another folder. b) By default, it mirrors the Write Metadata permission. c) It only applies to folders. d) If WriteMetadata is granted, then you should not deny WMM. 07. A platform administrator needs to retrieve from the metadata a complete LIBNAME statement including the user ID and password. To complete this task, the platform administrator must be connected to SAS Management Console with what type of user access in the metadata? a) Access to the credentials associated with libraries created with the METALIB procedure. b) Access to credentials established by the LIBNAME engine. c) Access to credentials associated with users in the outbound login. d) Access to credentials for the authentication domain associated with the database server. 08. The location of the repository manager physical files can be found in: a) SAS Management Console. b) the metadata server's omaconfig.xml file. c) the foundation repository. d) the metadata server's sasv9.cfg file. 09. Which statement regarding pre-assigned libraries is true? a) Pre-assigned libraries reduce the initialization time for a workspace server. b) Pre-assigned libraries always connect to an RDBMS at server initialization. c) Pre-assigned libraries always connect to a base SAS library at server initialization. d) Pre-assigned libraries do not have to be identical across all SAS client applications. 10. The SAS Web Application Server depends on which component? By default, it mirrors the WriteMetadata permission. a) SAS/CONNECT Spawner b) Cache Locator c) JMS Broker d) SAS Deployment Agent Answers: Question: 01: Answer: b Question: 02: Answer: a Question: 03: Answer: d Question: 04: Answer: c Question: 05: Answer: c Question: 06: Answer: a Question: 07: Answer: d Question: 08: Answer: b Question: 09: Answer: c Question: 10: Answer: b How to Register for SAS Platform Administrator Certification Exam? ● Visit site for Register SAS Platform Administrator Certification Exam.
0 Comments
10/19/2022 0 Comments Get Quality Preparation with SAS Platform Administrator (A00-250) CertificationSAS Platform Administrator certification questions and exam summary helps you to get focused on the exam. This guide also helps you to be on A00-250 exam track to get certified with good score in the final exam. SAS Platform Administrator (A00-250) Certification Summary
SAS Platform Administrator (A00-250) Certification Exam Syllabus Managing the SAS Environment [15%] - Secure a SAS platform configuration. Use operating system controls to protect the SAS configuration directory. - Update SAS Software Regularly manage and apply hot fixes. Apply SAS maintenance packs. Perform SAS license updates. - Work with the SAS Metadata Server. Configure the initial metadata server to use the network location for backups and the service login account. Configure the SAS Metadata Server cluster Install and configure additional metadata server nodes Manage metadata repositories Initial authentication to the metadata server Explain the importance of journaling - Promote metadata and associated content. Monitoring, Logging, and Troubleshooting SAS Servers [15%] - Monitor SAS servers. Monitor workspace servers and stored process servers. Use the SAS Environment Manager to view server resources. Set alerting and escalation functionality - Administer SAS server logging and modify logging configurations. Change logging levels and locate logs. Enable trace logging. Explain the difference between default logging and customized logging. Utilize dynamic logging. - Troubleshoot basic SAS server issues such as server availability. Utilize alerts for monitoring - Identify the properties and functionality of SAS servers. Identify startup order of SAS servers. Explain the functionality of the object spawner. Use the Server Manager plug-in to monitor SAS servers. Use Environment Manager to evaluate the resources available on the SAS servers. Backing Up the SAS Environment [8%] - Backup and restore the SAS environment. View backup and recovery history. Run an immediate (ad hoc) backup. Customize backups. View information about backup and recovery sources. View and modify the backup schedule. Perform full or partial recovery from one of the backups. Determine when to specify a central vault location. Explain the limitations of the Deployment Backup and Recovery tool. Use the SAS Backup Manager in Environment Manager to perform backups. Use the Roll forward option with metadata backups. Explain the role of the Deployment agent in the backup. Use scripts and system utilities to backup metadata - Backup and restore Metadata. Run an immediate (ad hoc) backup. Recover the metadata. Use the backup facility in SAS Management Console. Configure the backup properties. View and modify the backup schedule. Reorganize properties. Administering Users [22%] - Manage connection profiles. - Register users and groups in the metadata. Manage administrative access to the metadata. Manage roles Manage internal SAS accounts - Determine when to store passwords in the metadata - Give users access to processing servers and data servers - Identify SAS server authentication mechanisms. Administering Data Access [20%] - Register libraries and tables in the metadata. - Update table metadata. - Pre-assign a library. - Troubleshoot data access problems. - Use the metadata LIBNAME engine. Managing Metadata Authorization [20%] - Identify how the metadata authorization layer interacts with other security layers. - Identify where, how, and to whom metadata permissions are assigned. - Determine the outcome of metadata authorization decisions. - Use metadata permissions to secure metadata Use the metadata folder structure to manage access to metadata. - Create and use Access Control Templates. SAS Platform Administrator (A00-250) Certification Questions 01. The SAS Web Infrastructure Platform Data Serverstores content collected by the SAS Environment Agent in what format? a) Gemfire b) SAS Data Sets c) PostgreSQL d) SAS Log 02. A platform administrator needs to retrieve from the metadata a complete LIBNAME statement including the user ID and password. To complete this task, the platform administrator must be connected to SAS Management Console with what type of user access in the metadata? a) Access to the credentials associated with libraries created with the METALIB procedure. b) Access to credentials established by the LIBNAME engine. c) Access to credentials associated with users in the outbound login. d) Access to credentials for the authentication domain associated with the database server. 03. Which procedure allows a platform administrator to update table metadata? a) METAUPDATE_RULE b) METASELECT c) METATABLE d) METALIB 04. By default, which groups have WriteMetadata on the Foundation repository? a) PUBLIC b) SASUSERS c) ADMINISTRATORS ONLY d) SAS SYSTEM SERVICES ONLY 05. The SAS Web Application Server depends on which component? By default, it mirrors the WriteMetadata permission. a) SAS/CONNECT Spawner b) Cache Locator c) JMS Broker d) SAS Deployment Agent 06. Which statement is FALSE regarding the WriteMemberMetadata (WMM) permission? a) WMM is inherited from one folder to another folder. b) By default, it mirrors the Write Metadata permission. c) It only applies to folders. d) If WriteMetadata is granted, then you should not deny WMM. 07. Every SAS platform implementation includes: a) a foundation repository and a repository manager. b) a foundation repository and a custom repository. c) a custom repository and a repository manager. d) multiple project repositories. 08. The location of the repository manager physical files can be found in: a) SAS Management Console. b) the metadata server's omaconfig.xml file. c) the foundation repository. d) the metadata server's sasv9.cfg file. 09. Given the following authorization settings for Library Sales2:- Library Sales2's parent folder has an explicit grant of RM for Mary.- Library Sales2 has an explicit denial of RM for PUBLIC.Which statement is true? a) Mary can see Library Sales2. b) Mary can see data flagged as PUBLIC in Library Sales2. c) Mary cannot see Library Sales2. d) Mary can see Library Sales2, but not any data flagged as PUBLIC. 10. Which statement regarding pre-assigned libraries is true? a) Pre-assigned libraries reduce the initialization time for a workspace server. b) Pre-assigned libraries always connect to an RDBMS at server initialization. c) Pre-assigned libraries always connect to a base SAS library at server initialization. d) Pre-assigned libraries do not have to be identical across all SAS client applications. Answers: Question: 01: Answer: c Question: 02: Answer: d Question: 03: Answer: d Question: 04: Answer: b Question: 05: Answer: b Question: 06: Answer: a Question: 07: Answer: a Question: 08: Answer: b Question: 09: Answer: c Question: 10: Answer: c How to Register for SAS Platform Administrator Certification Exam? Visit site for Register SAS Platform Administrator Certification Exam. SAS Big Data Professional certification questions and exam summary helps you to get focused on the exam. This guide also helps you to be on A00-220 exam track to get certified with good score in the final exam. SAS Big Data Professional (A00-220) Certification Summary
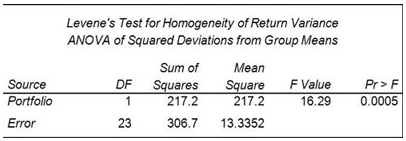
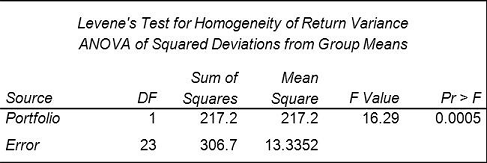
SAS Big Data Professional (A00-220) Certification Exam Syllabus 01. Data Management - 50% Navigate within the Data Management Studio Interface - Register a new QKB - Create and connect to a repository - Define a data connection - Specify Data Management Studio options - Access the QKB - Create a name value macro pair - Access the business rules manager - Access the appropriate monitoring report - Attach and detach primary tabs Create, design and be able to explore data explorations and interpret results Define and create data collections from exploration results Create and explore a data profile - Create a data profile from different sources (text file, filtered table, SQL query) - Interpret results (frequency distribution & pattern) - Use collections from profile results Design data standardization schemes - Build a scheme from profile results - Build a scheme manually - Update existing schemes Create Data Jobs - Rename output fields - Add nodes and preview nodes - Run a data job - View a log and settings - Work with data job settings and data job displays - Best practices (how do you ensure that you are following a particular best practice): examples: insert notes, establish naming conventions - Work with branching - Join tables - Apply the Field layout node to control field order - Work with the Data Validation node: - Add it to the job flow - Specify properties/review properties - Edit settings for the Data Validation node - Work with data inputs - Work with data outputs - Profile data from within data jobs - Interact with the Repository from within Data Jobs - Determine how data is processed - Data job variables - Set Sorting properties for the Data Sorting node - Set appropriate advanced properties options for the Data Sorting Node Apply a Standardization definition and scheme - Use a definition - Use a scheme - Be able to determine the differences between definition and scheme - Explain what happens when you use both a definition and scheme - Review and interpret standardization results - Be able to explain the different steps involved in the process of standardization Apply Parsing definitions - Distinguish between different data types and their tokens - Review and interpret parsing results - Be able to explain the different steps involved in the process of parsing - Use parsing definition Compare and contrast the differences between identification analysis and right fielding nodes - Review results - Explain the technique used for identification (process of the definition) Apply the Gender Analysis node to determine gender - Use gender definition - Interpret results - Explain different techniques for accomplishing gender analysis Create an Entity Resolution Job - Use a node in the data job that is the clustering node and explain why you would want to use it - Survivorship (surviving record identification) - Record rules - Field rules - Options for survivorship - Discuss and apply the Cluster Diff node - Apply Cross-field matching (new option) - Use the Match Codes Node to select match definitions for selected fields - Outline the various uses for match codes (join) - Use the definition - Interpret the results - Match versus match parsed - Explain the process for creating a match code - Select sensitivity for a selected match definition - Apply matching best practices Define and create business rules - Use Business Rules Manager - Create a new business rule - Name/label rule - Specify type of rule - Define checks - Specify fields - Distinguish between different types of business rules - Row - Set - Group - Apply business rules - Profile - Execute business rule node - Use of Expression Builder - Apply best practices Describe the organization, structure and basic navigation of the QKB - Identify and describe locale levels (global, language, country) - Navigate the QKB (tab structure, copy definitions, etc.) - Identify data types and tokens Be able to articulate when to use the various components of the QKB - Components include: - Regular expressions - Schemes - Phonetics library - Vocabularies - Grammar - Chop Tables Define the processing steps and components used in the different definition types - Identify/describe the different definition types - Parsing - Standardization - Match - Identification - Casing - Extraction - Locale guess - Gender - Patterns 02. ANOVA and Regression - 30% Verify the assumptions of ANOVA - Explain the central limit theorem and when it must be applied - Examine the distribution of continuous variables (histogram, box-whisker, Q-Q plots) - Describe the effect of skewness on the normal distribution - Define H0, H1, Type I/II error, statistical power, p-value - Describe the effect of sample size on p-value and power - Interpret the results of hypothesis testing - Interpret histograms and normal probability charts - Draw conclusions about your data from histogram, box-whisker, and Q-Q plots - Identify the kinds of problems may be present in the data: (biased sample, outliers, extreme values) - For a given experiment, verify that the observations are independent - For a given experiment, verify the errors are normally distributed - Use the UNIVARIATE procedure to examine residuals - For a given experiment, verify all groups have equal response variance - Use the HOVTEST option of MEANS statement in PROC GLM to asses response variance Analyze differences between population means using the GLM and TTEST procedures - Use the GLM Procedure to perform ANOVA - CLASS statement - MODEL statement - MEANS statement - OUTPUT statement - Evaluate the null hypothesis using the output of the GLM procedure - Interpret the statistical output of the GLM procedure (variance derived from MSE, F value, p-value R 2 , Levene's test) - Interpret the graphical output of the GLM procedure - Use the TTEST Procedure to compare means Perform ANOVA post hoc test to evaluate treatment affect - use the LSMEANS statement in the GLM or PLM procedure to perform pairwise comparisons - use PDIFF option of LSMEANS statement - use ADJUST option of the LSMEANS statement (TUKEY and DUNNETT) - Interpret diffograms to evaluate pairwise comparisons - Interpret control plots to evaluate pairwise comparisons - Compare/Contrast use of pairwise T-Tests, Tukey and Dunnett comparison methods - PLM Detect and analyze interactions between factors - Use the GLM procedure to produce reports that will help determine the significance of the interaction between factors. - MODEL statement - LSMEANS with SLICE=option (Also using PROC PLM) - ODS SELECT - Interpret the output of the GLM procedure to identify interaction between factors: - p-value - F Value - R Squared - TYPE I SS - TYPE III SS Fit a multiple linear regression model using the REG and GLM procedures - Use the REG procedure to fit a multiple linear regression model - Use the GLM procedure to fit a multiple linear regression model Analyze the output of the REG, PLM, and GLM procedures for multiple linear regression models - Interpret REG or GLM procedure output for a multiple linear regression model: convert models to algebraic expressions - Convert models to algebraic expressions - Identify missing degrees of freedom - Identify variance due to model/error, and total variance - Calculate a missing F value - Identify variable with largest impact to model - For output from two models, identify which model is better - Identify how much of the variation in the dependent variable is explained by the model - Conclusions that can be drawn from REG, GLM, or PLM output: (about H0, model quality, graphics) Use the REG or GLMSELECT procedure to perform model selection - Use the SELECTION option of the model statement in the GLMSELECT procedure - Compare the different model selection methods (STEPWISE, FORWARD, BACKWARD) - Enable ODS graphics to display graphs from the REG or GLMSELECT procedure - Identify best models by examining the graphical output (fit criterion from the REG or GLMSELECT procedure) - Assign names to models in the REG procedure (multiple model statements) Assess the validity of a given regression model through the use of diagnostic and residual analysis - Explain the assumptions for linear regression - From a set of residuals plots, asses which assumption about the error terms has been violated - Use REG procedure MODEL statement options to identify influential observations (Student Residuals, Cook's D, DFFITS, DFBETAS) - Explain options for handling influential observations - Identify colinearity problems by examining REG procedure output - Use MODEL statement options to diagnose collinearity problems (VIF, COLLIN, COLLINOINT) Perform logistic regression with the LOGISTIC procedure - Identify experiments that require analysis via logistic regression - Identify logistic regression assumptions - logistic regression concepts (log odds, logit transformation, sigmoidal relationship between p and X) - Use the LOGISTIC procedure to fit a binary logistic regression model (MODEL and CLASS statements) Optimize model performance through input selection - Use the LOGISTIC procedure to fit a multiple logistic regression model - LOGISCTIC procedure SELECTION=SCORE option - Perform Model Selection (STEPWISE, FORWARD, BACKWARD) within the LOGISTIC procedure Interpret the output of the LOGISTIC procedure - Interpret the output from the LOGISTIC procedure for binary logistic regression models: Model Convergence section Testing Global Null Hypothesis table Type 3 Analysis of Effects table Analysis of Maximum Likelihood Estimates table Association of Predicted Probabilities and Observed Responses 03. Visual Data Exploration - 20% Examine, modify, and create data items - Create and use parameterized data items - Examine data item properties and measure details - Change data item properties - Create custom sorts - Create distinct counts - Create aggregated measures - Create calculated items - Create hierarchies - Create custom categories Select and work with data sources - Work with multiple data sources - Change data sources - Refresh data sources Create, modify, and interpret automatic chart visualizations in Visual Analytics Explorer - Identify default visualizations - Identify the properties available in an automatic chart Create, modify, and interpret graph and table visualizations in Visual Analytics Explorer - Work with list table visualizations - Work with crosstab visualizations - Work with bar chart visualizations - Work with line chart visualizations - Work with scatter plot visualizations - Work with bubble plot visualizations - Work with histogram visualizations - Work with box plot visualizations - Work with heat map visualizations - Work with geo map visualizations - Work with treemap visualizations - Work with correlation matrix visualizations Enhance visualizations with analytics within Visual Analytics Explorer - Add fit lines to visualizations - Create forecasts - Interpret word clouds Interact with visualizations and explorations within Visual Analytics Explorer - Control appearance of visualizations within explorations - Add comments to visualizations and explorations - Use filters on data source and visualizations - Share explorations - Share visualizations SAS Big Data Professional (A00-220) Certification Questions01. How are the Field name analysis and Sample data analysis methods similar? a) They both utilize a match definition from the Quality Knowledge Base. b) They both require the same identification analysis definition from the Quality Knowledge Base. c) They both utilize an identification analysis definition from the Quality Knowledge Base. d) They both require the same match definition from the Quality Knowledge Base. 02. Using SAS Visual Analytics Explorer, a content developer would like to examine the relationship between two measures with high cardinality. Which visualization should the developer use? a) Scatter Plot b) Heat Map c) Scatter Plot Matrix d) Treemap 03. In SAS Visual Analytics Explorer, when a date data item is dragged onto an Automatic Chart visualization either a bar chart or a line chart will be created. What determines the type of chart created? a) The format applied to the date data item determines the type of chart displayed. b) A bar chart is created if the Model property of the data item is set to Discrete, and a line chart is created if the Model property is set to Continuous. c) The properties associated with the automatic chart determines the type of chart displayed. d) A line chart is created if the Model property of the data item is set to Discrete, a bar chart is created if the Model property is set to Continuous. 04. Which option in the properties of a Clustering node allows you to identify which clustering condition was satisfied? a) Condition matched field prefix b) Cluster condition field matched c) Cluster condition field count d) Cluster condition met field 05. A financial analyst wants to know whether assets in portfolio A are more risky (have higher variance) than those in portfolio B. The analyst computes the annual returns (or percent changes) for assets within each of the two groups and obtains the following output from the GLM procedure: Which conclusion is supported by the output?
a) Assets in portfolio A are significantly more risky than assets in portfolio B. b) Assets in portfolio B are significantly more risky than assets in portfolio A. c) The portfolios differ significantly with respect to risk. d) The portfolios do not differ significantly with respect to risk. 06. A Data Quality Steward creates these items for the Supplier repository: - A row-based business rule called Monitor for Nulls - A set-based business rule called Percent of Verified Addresses - A group-based rule called Low Product Count - A task based on the row-based, set-based, and group-based rules called Monitor Supplier Data Which one of these can the Data Quality Steward apply in an Execute Business Rule node in a data job? a) set-based business rule called Percent of Verified Addresses b) row-based business rule called Monitor for Nulls c) group-based rule called Low Product Count d) task based on the row-based, set-based, and group-based rules called Monitor Supplier Data 07. How do you access the Data Management Studio Options window? a) from the Tools menu b) from the Administration riser bar c) from the Information riser bar d) in the app.cfg file in the DataFlux Data Management Studio installation folder 08. When selecting variables or effects using SELECTION=BACKWARD in the LOGISTIC procedure, the business analyst's model selection terminated at Step 3. What happened between Step 1 and Step 2? a) DF increased. b) AIC increased. c) Pr > Chisq increased. d) - 2 Log L increased. 09. A sample of data has been clustered and found to contain many multi-row clusters. To construct a "best" record for each multi-row cluster, you need to select information from other records within a cluster. Which type of rule allows you to perform this task? a) Clustering rules b) Record rules c) Business rules d) Field rules 10. A linear model has the following characteristics: - a dependent variable (y) - one continuous predictor variables (x1) including a quadratic term (x12) - one categorical predictor variable (c1 with 3 levels) - one interaction term (c1 by x1) Which SAS program fits this model? a) proc glm data=SASUSER.MLR; class c1; model y = c1 x1 x1sq c1byx1 /solution; run; b) proc reg data=SASUSER.MLR; model y = c1 x1 x1sq c1byx1 /solution; run; c) proc glm data=SASUSER.MLR; class c1; model y = c1 x1 x1*x1 c1*x1 /solution; run; d) proc reg data=SASUSER.MLR; model y = c1 x1 x1*x1 c1*x1; run; Answers: Question: 01: Answer: c Question: 02: Answer: b Question: 03: Answer: b Question: 04: Answer: a Question: 05: Answer: c Question: 06: Answer: b Question: 07: Answer: a Question: 08: Answer: d Question: 09: Answer: d Question: 10: Answer: c How to Register for SAS Big Data Professional Certification Exam? Visit site for Register SAS Big Data Professional Certification Exam. 11/29/2021 0 Comments Get Quality Preparation with SAS Visual Business Analytics (A00-278) CertificationSAS Visual Business Analytics certification questions and exam summary helps you to get focused on the exam. This guide also helps you to be on A00-278 exam track to get certified with good score in the final exam. SAS Visual Business Analytics (A00-278) Certification Summary
SAS Visual Business Analytics (A00-278) Certification Exam Syllabus 01.Data Sources and Data Items (29%) Import data into SAS Visual Analytics - Import local data - Import server data (Oracle, Hadoop, SAS) - Import social media data - Differentiate between local, server, and social media data imports Examine, modify, and create data items - Create and use parameterized data items - Examine data item properties and measure details - Change data item properties - Create custom sorts - Create distinct counts - Create aggregated measures - Create calculated items - Create hierarchies - Create custom categories Select and work with data sources - Work with multiple data sources - Change data sources - Refresh data sources 02. Analyzing Data (21%) Create, modify, and interpret automatic chart objects for analyzing data - Identify the options available in an automatic chart Create, modify, and interpret graph and table objects for analyzing data - Work with list table object - Work with crosstab object - Work with bar chart object - Work with line chart object - Work with scatter plot object - Work with bubble plot object - Work with histogram object - Work with box plot object - Work with heat map object - Work with geo map object - Work with treemap object - Work with correlation matrix object - Work with bubble change plot object - Work with time series plot object Create, modify, and interpret data analysis using report objects (i.e. adding fit lines, forecasting, network, path and text analysis objects, etc.) - Add fit lines to scatter plot and heat map object - Work with forecasting object - Work with network analysis object - Work with path analysis object - Work with text analytics object Interact with objects for analyzing data - Control appearance of objects (options, ranks, display rules, sorting, etc.) - Use filters on data source and objects - Export data and images from objects 03. Building Reports (50%) Create and modify list tables and crosstabs to build a report - Create and modify list tables - Create table display rules - Add sparklines - Create and modify crosstabs - Manipulate columns - Change options for tables and crosstabs - Create hierarchies from a crosstab - Create and modify display rules Create and modify graphs to build a report - Create and modify bar charts, targeted bar charts, waterfall charts - Create and modify pie charts - Create and modify line charts - Create and modify scatter plots - Create and modify time series plots - Create and modify bubble plots - Create and modify treemap - Create and modify dual axis charts - Create and modify key values - Create and modify word cloud - Create and modify butterfly chart - Adjust options for graphs - Create and modify geography maps - Create and modify gauges Create and modify controls, containers, and content to build a report - Place report objects in containers - Given a scenario, select the appropriate container (stacking, prompt, etc.) - Add text report objects - Include dynamic text in a text object - Add image report objects - Add controls to reports - Given a scenario, apply the proper controls Design a report using pages and layouts - Layout the report and pages - Move, duplicate, and change report objects - Create and work with pages - Modify report options Add actions, filters, ranks and alerts to reports - Add actions within page - Add links to other reports - Add external links - Add filters and ranks to report objects - Add page prompts and report prompts - Add actions to reports - Work with parameters Share and print reports - Distribute reports - Print reports - Email reports SAS Visual Business Analytics (A00-278) Certification Questions 01. Which option is NOT found in the File Specifications section when importing a delimited text file? a) Specify the input file delimiter. b) Specify the number of scanned rows. c) Specify the range of imported rows and columns. d) Specify the source encoding. 02. Which statements pertaining to multiple data sources in a report are TRUE? (Choose two.) a) Different objects on a page can use data items from either data source in their roles. b) A report prompt can be applied to different data sources if the prompted data item can be mapped between the data sources. c) A data source filter on one of the data sources can be applied to all data sources through data actions. d) Cardinality thresholds for a report limit the number of rows processed in each of the data sources 03. Which statement is TRUE about report alerts? a) Alert notifications can be sent to subscribers via email. b) Alert notifications are only sent to the user that created the alert. c) Alert notifications are only sent when the report is open. d) Alerts can be set on an individual object and the entire report. 04. Which object supports adding a sparkline? a) Crosstab b) Time series plot c) Line chart d) List table 05. Which part of the user interface allows you to change the classification of a measure data item? a) You cannot change the classification of a measure data item. b) Right-click the data item in the Data pane and select Convert to category. c) Select Options in the Data pane and select Change classification. d) Use the Category role in the Roles pane. 06. Which statement is TRUE when importing Microsoft Office Access files into SAS Visual Analytics? a) All selected tables are imported. b) You can import one table at a time. c) You cannot import Microsoft Access files. d) All tables are imported. 07. What type of data items are required to create a dual axis bar-line chart? a) one category and one measure b) two categories c) two measures d) one category and two measures 08. Which option CANNOT be added to a scatter plot or heat map? a) Linear b) Quadratic c) Cubic d) BSpline 09. A content developer creates a display rule for a crosstab. What changes can the display rule apply to the crosstab? a) Rows can be color highlighted. b) Individual cells can be color highlighted. c) The brightness of the crosstab can be changed. d) The crosstab can be hidden if no results are returned by the display rule. 10. How can a report designer create a page in a report that is not visible to the end user? a) Right-click the page name and select Hide Page. b) Remove all interactions from the pages. c) Edit the page authorizations and deny Read access. d) Change the foreground page color to white. Answers: Question: 01: Answer: c Question: 02: Answer: a, b Question: 03: Answer: a Question: 04: Answer: d Question: 05: Answer: b Question: 06: Answer: c Question: 07: Answer: d Question: 08: Answer: d Question: 09: Answer: b Question: 10: Answer: a How to Register for SAS Visual Business Analytics Certification Exam? Visit site for Register SAS Visual Business Analytics Certification Exam. 11/28/2021 0 Comments Get Quality Preparation with SAS Big Data Professional (A00-221) CertificationSAS Big Data Professional certification questions and exam summary helps you to get focused on the exam. This guide also helps you to be on A00-221 exam track to get certified with good score in the final exam. SAS Big Data Professional (A00-221) Certification Summary
SAS Big Data Professional (A00-221) Certification Exam Syllabus 01. SAS and Hadoop - 30% Describe the baseline requirements for interacting with Hadoop - SAS_HADOOP_JAR_PATH and SAS_HADOOP_CONFIG_PATH environment variables - JAR file requirements - Hadoop XML configuration file contents - JAR files and XML files must be accessible to the SAS Server - Understand the precedence of settings for Hadoop XML configuration files - Identify the components of a SAS and Hadoop solution - List the communication paths between the components of a SAS and Hadoop solution Use the HADOOP procedure and the Hadoop FILENAME statement to interact with Hadoop from a SAS session - Know which HDFS commands are available through the Hadoop procedure - Submit HDFS file system commands (DELETE, MKDIR, RENAME, CHMOD, LS, CAT) - Copy files between SAS and Hadoop via COPYFROMLOCAL and COPYTOLOCAL statement - Submit MapReduce programs with the MAPREDUCE statement - Understand best practice considerations when using the FILENAME statement - use the FILENAME statement to read data from and write data to the Hadoop file system in a SAS DATA step - Execute Pig code with the PIG statement in the HADOOP procedure Query and manage Hive tables stored in Hadoop using explicit SQL pass-through - Manage connections to Hive with the CONNECT/DISCONNECT statements (schema, server, username, password, etc) - Access Hive metadata via SHOW and DESCRIBE statements - Select data from tables with HiveQL (select, from, where clauses) - Join tables with HiveQL - Use both HiveQL and SAS SQL features (ORDER BY, functions, labels) in the same SQL procedure SELECT statement - Create SAS data sets and views from Hive results - String dates vs. SAS dates - Using the CAST function to control data type in explicit queries (32k string lengths) - Create Hive table definitions - Load data into Hive table defitions from local data - Load data into Hive table definitions from HDFS data - Control length of character variables created in Hive tables - Work with Hive string types in SAS - Control Hive table properties with TBLPROPERTIES statement (SASFMT or with data set option DBSASTYPE= option) - Compare managed and external Hive tables - Compare different Hive file types (textfile, sequencefile). Use of SERDEs - Use data set options to define specific HDFS file types Work with Hadoop files using the SAS/ACCESS LIBNAME statement - Write a LIBNAME statement to access Hive tables - Access Hive metadata using LIBNAME statement and the CONTENTS procedure - Understand that the SAS/ACCESS engine writes database-specific SQL code when using implicit pass-through - Maximize the use of HiveQL by optimzing implicit pass-through (summarization, subsetting, joins) - Use system options to determine where processing occurs (SASTRACE, NOSTSUFFIX, SASTRACELOC) - Evaluate SAS logs to determine the amount of implicit pass-through performed by a SAS program - Identify SAS data set options that can be implicitly passed to Hive - Identify SAS functions that can be passed to Hive - Convert date formats with the SASDATEFMT= data set option - Embed LIBNAME statements in SQL View defintions - Identify best practices when combining tables to maximize Hive usage - Methods to combine/join tables - Copy data sets to Hive using the COPY procedure - Identify advantages of using SAS/ACCESS LIBNAME method - Identify disadvantages of using SAS/ACCESS LIBNAME method - Maximize performance when using the LIBNAME statement - Efficient methods for BY GROUP processing with in-database procedures - Managing data types for computed columns. - Partition and cluster Hive tables - Create Hive external tables 02. SAS DS2 Programming - 30% Write DS2 programs - Utilize run group processing - Use DATA, ENDDATA, and RUN statements properly - Use system methods, INIT(), RUN(), TERM() - Build user defined methods - Pass arguments to user defined methods - Explain the use of the INIT(), RUN(), TERM() system methods - Use the OVERWRITE option - Understand how DS2 handles reserved keywords - Recognize components of traditional DATA Step programming that are or are not supported in DS2 Read data using DS2 - read data with a SET statement - write FedSQL code within SET statements to read data - Use FedSQL SELECT statements to extract specific variables from input data sets - Use FedSQL Join statements to merge data from multiple input data sets - Use FedSQL WHERE statements to extract specific observations from input data sets - Use the MERGE statement to join data. - Subset data using subsetting IF statements - Read table data with a BY statement, without pre-sorting the data - Use a FedSQL query with an ORDER BY clause to provide sorted data to the SET statement for BY group processing Work with variables, arrays, and ANSI SQL data types - Define and use local and global variables (understand scope, what goes into PDV, output data sets) - Declare variables with the DCL statement - Use fractional, integer, character and Date & Time ANSI SQL data types - Use CHAR, NCHAR, VARCHAR, NVARCHAR character data types - Use DECIMAL, DOUBLE, FLOAT, REAL fractional numeric data types - Use BIGINT, INTEGER, SMALLINT, TINYINT interger numeric data types - Use BINARY, VARBINARY binary data types - Use DATE, TIME, TIMESTAMP date and time data types - Identify coercible and non-coercible data types - Understand autoconversion of DS2 data types when DS2 variables are output to SAS data sets - Select variables with KEEP and DROP statements and KEEP= and DROP= options - Understand how SAS will perform automatic type conversions - DS2SCOND option statement - Use ANSI quoting standards in variable assignment statements - Use macro variables within ANSI quoted variable assignment statements (%TSLIT macro) - set variable attributes (Length, format, informat) within variable declaration statements - Use the VARARRAY statement to declare arrays - Use the DCL staement to declare temporary arrays - Assign values to array variables - Understand the difference between SAS MISSING and ANSI NULL data values - Invoke ANSI data processing mode for NULL values with the ANSIMODE option Use expressions and functions in DS2 programs - Use the DS2 IF expression in place of IF/THEN conditional statements - Use the DS2 LIKE expression to compare character values to specific patterns - Convert SAS datetime variables to DS2 ANSI TIMESTAMP variables with the TO_TIMESTAMP function - Convert SAS date variables to DS2 ANSI DATE variables with the TO_DATE function - Convert SAS time variables to DS2 ANSI TIME variables with the TO_TIME function - Convert DS2 ANSI DATE, TIME, and TIMESTAMP variables to SAS date, time and datetime variables with the TO_DOUBLE function - Increment date and time values with the INTDT and INTTS functions - Execute FedSQL statements with the SQLEXEC function Work with Methods, Packages, and Threads - Create methods that modify parameters at the site by using IN_OUT variables - Create methods that return a value using a RETURN statement - Overload methods by creating methods with multiple signatures - Create user defined packages with the PACKAGE statement - Understand the capabilities of predefined DS2 packages (such as FCMP, SQLSTMT, HASH, JSON) - Intantiate DS2 packages with the DECLARE statement - Use threading to alleviate CPU bound processes - Create threads using the THREAD statement - Declare instances of threads in a DS2 program - Call threads using a SET FROM statement - Specify the number of threads using a THREADS= option - How to run threads inside parallel databases - DS2ACCEL = YES option - Requirements to execute DS2 code in-database 03. Hadoop Programming - 15% Describe the Hadoop architecture - Identify Hadoop elements such as Name Nodes, Data Nodes, Job Trackers, Task Trackers, YARN - Explain Hadoop concepts such as distributed storage & processing, splits, replication, MapReduce - Describe components of the Hadoop ecosystem (Hive, Pig, Sqoop) - Describe attributes of big data - Identify use cases for Hadoop Manipulate and load data files using command line tools - Use Linux shell commands (ls -ltr/pwd/mkdir/cd) - Load and manipulate data into Hadoop using Linux commands (hdfs dfs - mkdir/put/copyFromLocal/ls/cat) - Use Sqoop to move data from a RDBMS into Hadoop Write Hive programs to create, join, and query data tables - Create databases and tables in Hive - Understand the difference between external and internal tables - Work with Hive variable types - Load data into Hive table definitions with LOAD and INSERT statements - Recognize challenges when importing data (embedded delimiter characters, header values) - Limit values returned by a Hive query with the SELECT.....LIMIT keyword - Sort Hive query results with the SELECT...ORDER BY keyword - Group Hive query results with the GROUP BY keyword - Choose which values to select from a data table using the SELECT WHERE keyword - Retrieve unique values with the SELECT DISTINCT - Join tables (Inner, Outer, Left, Right) - Use functions in Hive queries (sum, count, avg, max, min, round, floor, ceil, rand, concat, substr, upper, ucase, lower, lcase, trim) - Use relational and arithmetic operators in Hive queries Write Pig programs to perform ETL tasks and to analyze large data sets - Identify Pig data types - Build Pig programs with LOAD, FOREACH/GENERATE, FILTER, SPLT, LIMIT, UNION, DISTINCT, ORDER, GROUP, STORE, DUMP keywords - Use name and positional references in Pig programs - Identify valid identifiers (start with letter, then letters, digits, underscores) - Use Arithmetic, String, and Boolean Expressions - Use the CAST operator to change variable types - Increase parallel processing with the PARALLEL keyword - Combine data from multiple tables with INNER, LEFT, RIGHT, and OUTER JOIN keywords - Combine data using special join types: REPLICATED, SKEWED, MERGE - Use parameters in a Pig program - Use Diagnostic operators: DESCRIBE, EXPLAIN, DUMP, ILLUSTRATE - Use functions in Pig programs - EVAL Functions: AVG, SUM, CONCAT, COUNT, COUNT_STAR, IsEmpty, MIN, MAX, SIZE, SUBTRACT, TOKENIZE - DATE Functions: CurrentTime, DaysBetween, HoursBEtween, GetDay, GetHour (etc.), AddDuration, ToUnixTime, ToDate, ToMilliSeconds, ToString - String Functions: STARTSWITH, ENDSWITH, REGEX_EXTRACT, REPLACE, TRIM, LTRIM, RTIM, INDEXOF, LAST_INDEX_OF, LOWER, UPPER, LCFIRST, UCFIRST SUBSTRING, EqualsIgnoreCase - Math Functions: ABS, ACOS, ATAN (etc) SQRT, CBRT, Exp, CEIL, FLOOR, LOG, LOG10, RANDOM, ROUND - Tuple, Bag, Map functions: TOTuPLE, TOBAG, TOMAP, TOP - Register and use User Defined Functions 04. Data manipulation with the IMSTAT procedure - 25% Execute IMSTAT procedures - Define a SASIOLA library to access in-memory data in a LASR Analytic Server - Describe the key functionality of the IMSTAT procedure - Perform one-dimensional numerical exploration with IMSTAT procedure statements SUMMARY and FREQUENCY - Perform two-dimensional numerical exploration using the CROSSTAB or GROUPBY=option Perform actions required to produce graphs with PROC IMSTAT - Use PROC IMSTAT statements and options that calculate summary statistics for graphing - Transfer the summary statistics tables to the SAS server Manipulate In-Memory Data - Define WHERE clauses to explore subsets of an in-memory table - Create permanent columns using the COMPUTE statement - Create temporary columns using temporary expressions of computed columns - Work with SAS formats in the IMSTAT procedures - Use the Fetch statement to retrieve data from an in-memory table - Join in-memory tables Use High-Performance procedures with the SAS LASR Analytic Server - Compare the SAS High-Performance procedures and SAS IN-Memory Statistics - Use the HPIMPUTE procedure to add imputed columns to an in-memory table SAS Big Data Professional (A00-221) Certification Questions 01. The following SAS program is submitted: proc ds2; data work.sasorders; dcl timestamp order_timestamp; dcl double order_datetime; method run(); set orders; order_timestamp = to_timestamp(order_datetime); end; enddata; run; quit; What happens when the program is executed? a) The variable order_timestamp is created and processed as an ANSI timestamp value in the DS2 program. The order_timestamp value is converted to a SAS datetime when it is written to the output SAS data set. b) The variable order_timestamp is created and processed as an ANSI timestamp value in the DS2 program. The output data set stores the values as a SAS timestamp value. c) The variable order_timestamp is converted to a SAS time value. The output data set stores this as the number of seconds since midnight. d) The program does not execute because order_datetime is a SAS datetime value. 02. Which statement creates a temporary array within DS2? a) vararray double a[2]; b) vararray double a(2); c) array a(2) s1-s2; d) dcl double a[2]; 03. What is an advantage of using a LIBNAME statement to interact with your Hadoop cluster? a) It enables you to submit user-written HiveQL code to Hive. b) The GENERATE_PIG_CODE= option enables you to bypass Hive and generate Pig Latin code. c) It enables some SAS procedures to push processing into Hive. d) It ensures that Hive will handle all processing. 04. Web server logs are written in an HDFS directory. The following lines indicate the format and an example of the comma-separated values for one line in the log file. # IP address, timestamp, request, status, size 192.168.12.41,24/Nov/2015:10:09:58 -0500, "GET /services/config.xml HTTP/ Which CREATE TABLE statement enables a Hive query to access each of the fields? a) create external table weblogs (ip string, dt string, req string, status int, sz string) row format delimited fields terminated by ',' location '/data/weblogs'; b) create external table weblogs (ip string, dt string, req string, status int, sz string) fields terminated by ',' location '/data/weblogs'; c) create external table weblogs (ip string, rest string) row format delimited fields terminated by ',' location '/data/weblogs'; d) create external table weblogs (ip string, dt string, req string, status int, sz string) fields delimited fields by ',' location '/data/weblogs'; 05. In the example below, the input data set is a Hive table accessed using a SAS/ACCESS to Hadoop LIBNAME statement. proc freq data=hivelib.myhivetable; class month; by year; run; Which statement is true about this program? a) The procedure will fail unless the table HIVELIB.MYHIVETABLE is already stored ordered by YEAR. b) SAS will generate a HiveQL query to return the data to SAS ordered by YEAR so that the procedure receives the data ordered by YEAR as required. c) BY statements do not require the data be received by the procedure in any specific order. d) BY statements are not supported for Hive tables because it is not possible to order data that is distributed on different nodes of the Hadoop cluster. 06. Which operator is NOT a diagnostic operator for testing a Pig program? a) DUMP b) ILLUSTRATE c) EXPLAIN d) SPLIT 07. Refer to the log message shown below: 58 proc ds2; 59 data test; 60 dcl double date; 61 method run(); 62 set work.one; 63 mm=2; 64 end; 65 enddata; 66 run; ERROR: Compilation error. ERROR: Parse encountered type when expecting identifier. ERROR: Parse failed on line 60: dcl double >>> date <<< ; NOTE: PROC DS2 has set option NOEXEC and will continue to prepare statements. 67 quit; Which of the following changes will fix the errors shown in the log? a) Replace line 60 with dcl double 'date'; b) Replace line 60 with dcl double "date"; c) Replace line 60 with dcl string date; d) Replace line 60 with dcl double 'date'n; 08. This question will ask you to provide a line of missing code. Which line of code would you insert to get the mean and standard deviation of INCOME and AGE, calculated separately for GENDER variable values F (female) and M (male)? proc imstat; table mylasr.bankdata(tag="&TagString"); <insert code here> run; a) crosstab income*gender age*gender; b) summary income age / by=gender; c) summary income age / groupby=gender; d) univariate income age / by=gender; 09. When working with data stored in Hadoop, which SAS function is NOT passed to Hive by default? a) DATE b) HOUR c) VAR d) UPCASE 10. Many temporary tables may be created in the LASR server by PROC IMSTAT analysis actions. What happens to temporary tables when a PROC IMSTAT session is terminated? a) All temporary tables are saved to the SAS server WORK library. b) All temporary tables are purged from the LASR server. c) The last temporary table created is saved to the SAS WORK library. d) The last temporary table created is saved to storage in the HDFS. Answers: Question: 01: Answer: a Question: 02: Answer: d Question: 03: Answer: c Question: 04: Answer: a Question: 05: Answer: b Question: 06: Answer: d Question: 07: Answer: b Question: 08: Answer: c Question: 09: Answer: a Question: 10: Answer: b How to Register for SAS Big Data Professional Certification Exam? Visit site for Register SAS Big Data Professional Certification Exam. 11/16/2021 0 Comments Get Quality Preparation with SAS Data Integration Developer (A00-260) CertificationSAS Data Integration Developer certification questions and exam summary helps you to get focused on the exam. This guide also helps you to be on A00-260 exam track to get certified with good score in the final exam. SAS Data Integration Developer (A00-260) Certification Summary
SAS Data Integration Developer (A00-260) Certification Exam Syllabus Overview ● Define the architecture of the platform for SAS Business Analytics. ● Describe the available interfaces including: ○ SAS Data Integration Studio ○ DataFlux Data Management Studio ● Define the change management feature of SAS Data Integration Studio. ● Discuss the DataFlux Data Management Server. Creating Metadata for Source and Target Data ● Define administrative tasks to be performed for SAS Data Integration Studio. ● Describe the New Library Wizard. ● Use Register Tables wizard to register source data. ○ Use Register Tables wizard to register metadata for a Microsoft Access database table using ODBC. ● Use Register Tables wizard to register metadata for a Microsoft Access database table using ODBC. ● Register metadata for a comma-delimited external file. ● Import and Export Metadata. ○ Discuss SAS packages. ○ Discuss importing and exporting of relational metadata. Creating Metadata for Target Data and Jobs ● Describe features of the New Table wizard. ● Discuss components of Join's Designer window including: ○ Navigate pane ○ SQL clauses pane ○ Tables pane ○ Properties pane ● Investigate mapping and propagation. ● Work with performance statistics. ○ Enable/disable performance statistics. ○ Be able to view performance statistics. ● Generate reports on metadata for tables and jobs. ● Define Impact and Reverse Impact Analysis. ● Import SAS code. ○ Import macro-based SAS code. Working with Transformations ● Discuss and use the Extract and Summary Statistics transformation. ● Discuss and use the Loop transformations. ○ Iterate a job. ○ Iterate a transformation. ● Investigate where status handling is available. ● Explain the functionality of the Data Validation transformation. ○ Identify and configure the three types of validations. ○ Configure an error table and an exception table for data validation. ● Discuss and use the Rank, Transpose, Append, List and Sort transformations. ● Discuss and use the Apply Lookup Standardization transformation. ● Discuss and use the Compare Tables transformation. ● Discuss and use transformations in the SQL grouping of transformations. ● Apply and use the Standardize with Definition transformation. Working with Tables and the Table Loader Transformation ● Discuss reasons to use the Table Loader transformation. ● Discuss various load styles provided by the Table Loader transformation. ● Discuss various types of keys and how to define in SAS Data Integration Studio. ● Discuss indexes and how to define in SAS Data Integration Studio. ● Discuss Table Loader options for keys and indexes. ● Discuss the Bulk Table Loader transformation. ● Discuss and use the components of the Join’s Designer Window related to in database processing. Working with Slowly Changing Dimensions ● List the functions of the SCD Type 2 transformation. ● Define keys. (business, surrogate, and retained) ● Detect and track changes. ● Discuss the Lookup transformation. ● Discuss the SCD Type 1 Loader. Defining Generated Transformations ● Define SAS code transformation templates. ● Create a custom transformation Deploying Jobs ● Discuss the types of job deployment available for SAS Data Integration Studio Jobs. ● Provide an overview of the scheduling process. ● Discuss the types of scheduling servers. ● Discuss the Schedule Manager in SAS Management Console. ● Discuss batch servers. ● Describe deployment of SAS Data Integration Studio jobs as a SAS Stored Process. In Database Processing ● Define indatabase processing ○ List benefits of in-database processing ● Enable in-database processing. ● Define and discuss ELT methods ● Use a DBMS function in a SAS DI job SAS Data Integration Developer (A00-260) Certification Questions 01. Assume that you have completed the Register Tables wizard in SAS Data Integration Studio. Which statement is true? a) The physical table(s) selected are copied to the application server specified in the library. b) The physical table(s) selected are copied to the SAS Folders location specified in the wizard. c) Metadata for the physical table(s) selected is stored on the application server specified in the library. d) Metadata for the physical table(s) selected is stored in the SAS Folders location specified in the wizard. 02. In SAS Data Integration Studio, a business key can be defined in the properties of which transformation? a) Data Validation b) SQL Join c) Lookup d) SCD Type 2 Loader 03. Within SAS Data Integration Studio's Table Loader transformation, which load style choice does NOT exist? a) Delete where b) Append to Existing c) Replace d) Update/Insert 04. Which products are needed on the local host in order to access data from an MS Access Database using an ODBC Data Source name? a) SAS/ACCESS interface to DSN b) SAS/ACCESS interface to ODBC c) SAS/ACCESS interface to MDB d) SAS/ACCESS interface to PC Files 05. Which SAS Data Integration Studio reports, generated as external files, can be stored as document objects within metadata? a) only job reports b) only table reports c) both job reports and table reports d) No reports can be stored as document objects. 06. Which statement is true regarding external files? a) External file objects are accessed with SAS INFILE and FILE statements. b) External files contain only one record per line. c) External files can be used as input but not as outputs in SAS Data Integration Studio jobs. d) SAS can only work with Blank, Comma, Semicolon and Tab as delimiters in external files. 07. Within SAS Data Integration Studio's SQL Join transformation, the option to turn on debug is located in which Properties pane? a) Select Properties b) Create Properties c) SQL Join Properties d) Job Properties 08. You want to register an external file with the following structure: first line contains Customer First and Last Name second line is address1 third line is address 2 fourth line contains the phone number What action should you take to read this file? a) Use the New User Written External File wizard. b) Use the New Fixed Width External File wizard. c) Use the New Delimited External File wizard. d) Use the New COBOL Copybook wizard. 09. Which of the following servers is NOT a part of the platform for SAS Business Analytics server tier? a) SAS Metadata Server b) SAS Workspace Server c) SAS/CONNECT Server d) SAS Content Server 10. You want to create a job to extract only the rows that contain information about female employees from a table that contains information about both male and female employees.The new table should have observations in ascending order of age. Refer to the job flow diagram in the exhibit. Where would you set the options to filter and sort the data?
a) Where tab and Group By tab b) Where tab and Order By tab c) Where tab and Parameters tab d) Group By tab and Parameters tab Answers: Question: 01: Answer: d Question: 02: Answer: d Question: 03: Answer: a Question: 04: Answer: b Question: 05: Answer: c Question: 06: Answer: a Question: 07: Answer: c Question: 08: Answer: a Question: 09: Answer: d Question: 10: Answer: b How to Register for SAS Data Integration Developer Certification Exam? Visit site for Register SAS Data Integration Developer Certification Exam. SAS Visual Modeling certification questions and exam summary helps you to get focused on the exam. This guide also helps you to be on A00-274 exam track to get certified with good score in the final exam. SAS Visual Modeling (A00-274) Certification Summary
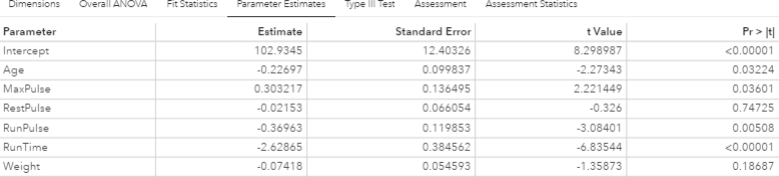
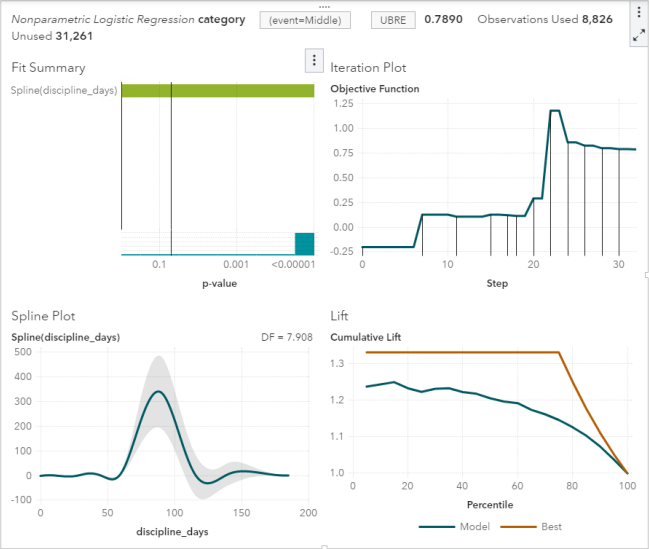
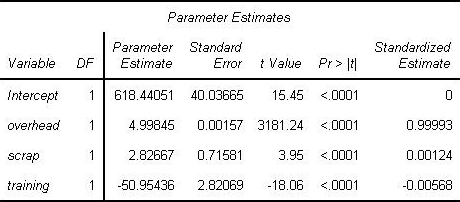
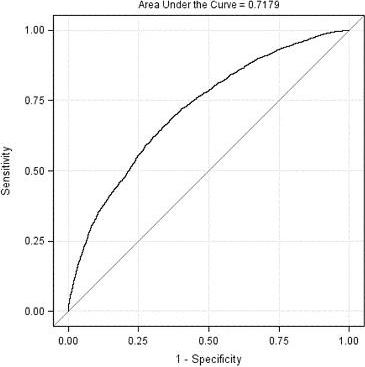
SAS Visual Modeling (A00-274) Certification Exam Syllabus 01. SAS® Visual Statistics Cross-functional Tasks - 18% Prepare data using SAS® Visual Analytics. - Manage explorations and visualizations. - Impute a variable. - Transform a variable. - Create an aggregated measure. - Replace dirty data with missing values. - Combine multiple categories into fewer levels. - Create dummy variables in SAS® Visual Analytics and SAS® Visual Data Builder. Filter data used for a model. - Exclude selections to filter data. - Apply filters to visualization and data source. - Review Measure Details. Use interactive group-by. - Explain group-by modeling. - Assign a group-by variable to a predictive model (logistic regression, linear regression model and generalized linear model). - Interactively examine the Fit Summary for group-by models. - Choose the best fitting group-by model using fit statistics and Variable Importance. - Interpret model results using advanced group-by feature. - Examine the summary table for group-by processing. 02. Building and Assessing Segmentation Models - 32% Perform unsupervised segmentation using cluster analysis. - Explain unsupervised classification. - Given a scenario, set proper inputs for k-means algorithm. - Build a cluster analysis in SAS® Visual Statistics. - Assign roles for cluster analysis. - View and edit cluster properties. - Set Parallel Coordinate properties for a cluster. - Given a scenario, appropriately change the number of clusters. - Derive a cluster ID variable and use it in another visualization. Analyze cluster results. - Interpret a Cluster Matrix. - Interpret Parallel Coordinates plot. - Interpret Cluster Summary tab. Perform supervised segmentation using decision trees. - Explain how split points are determined. - Assign variable roles for a decision tree. - Define decision tree properties. - Describe how predictions are formulated for a decision tree. - Explain variable selection methods for decision trees. - Derive a leaf ID for use in other models. - Prune a decision tree. Asses decision tree results. - Interpret tree with Tree Map. - Interpret Leaf statistics. - Interpret Assessment panel. - Investigate leaf nodes. - Explain icicle plot. 03. Building and Assessing Regression-type Models - 40% Explain linear models. - Explain linear regression. - Model effects usage. - Given a scenario, determine when to use a linear regression model vs. a generalized linear model. Perform linear regression modeling. - Assign linear regression roles. - Add Interaction Effect. - Define linear regression properties. - Explain informative missingness. - Review outlier details and exclude outliers. Perform generalized linear regression modeling. - Assign generalized linear model roles. - Assign offset variable. - Define linear regression properties. - Link functions and distributions in generalized linear models. - Given a scenario, choose appropriate distribution and link function. Perform logistic regression modeling. - Explain logistic regression essentials. - Explain prediction in logistic regression. - Explain variable selection in SAS® Visual Statistics. - Specify which variable is the event (binary). - Specify how a multinomial response variable is used in SAS® Visual Statistics. - Assign logistic regression roles. - Define logistic regression properties. - Specify when to use appropriate link function when building a predictive model. Assess model results. - Interpret Fit Summary window. - Interpret Residual Plot. - Interpret ROC chart (KS Statistic). - Evaluate Misclassification plot. - Evaluate the Lift chart. - Interpret Influence plot. - Interpret Summary bar. - Assess residuals and other model diagnostics to choose an appropriate distribution and link function. - Derive predicted values and describe in terms of predicted probabilities in SAS® Visual Statistics. - Apply prediction cut-off. 04. Model Comparison and Scoring - 10% Compare models - Explain model comparison features. - Assign model comparison properties. - Interpret comparison results using Assessment panel, Fit Statistics, ROC charts, concordance statistics, misclassification, etc. - Interpret Summary Table for model comparison (statistics, variable importance). - Given a scenario, use a particular fit statistic to select a champion model. - Define the conditions that make models comparable in SAS® Visual Statistics. Score models - Explain scoring functionality. - Export score code. - Implement score code. - Identify which SAS® tools can score new data using score code generated by SAS® Visual Statistics. SAS Visual Modeling (A00-274) Certification Questions 01. You would like to compare multiple models that you've built in SAS Visual Statistics. Which parameters must be the same for all models being compared? (choose 3) a) Data Source b) Assessment Bins c) Model Type d) Event Level e) Response Variable f) Link Function 02. Your company has a dataset that represents global sales. You are a part of a team of analysts that each have responsibility for a certain region of the world. You decide to create a data source filter to suppress every region but yours. What effect will this have on any new explorations that your teammates create? a) It will delete all observations that do not match your region. b) It will have no effect on any observations in the dataset. c) It will suppress all observations that do not match your region. d) It will suppress all observations that do not match their corresponding region. 03. Which equation does NOT represent a linear model? Note: bi are parameters and Xi are variables. a) y = b0 + b1X1 + b2X2 b) y = b0 + b1X1 + b2X2 + b3(X1X2) c) y = b0 + b1X1 + (b2/b1)X2 d) y = b0 + b1X1 + b2X1 3 04. You perform a logistic regression on a multinomial response variable in SAS Visual Statistics that has 3 levels: Small, Medium, Large. "Large" is specified as the event. Which statement is true? a) The other levels are grouped into one non-event. b) An ordinal logistic regression is performed. c) A multinomial logistic regression is performed. d) The other levels are offset to account for exposure. 05. Refer to the exhibit from a linear regression model in SAS Visual Statistics. Based on the table above and assuming a significance level of 0.05, what can be concluded about the linear regression model? a) The Intercept is an important predictor of the response. b) RestPulse is a significant predictor of the response. c) For one one-unit increase in RunTime, there is an expected increase in the response of 2.6287. d) For a .03696 unit decrease in RunPulse, there is an expected one-unit increase in the response. 06. Refer to the exhibit: Which option was not specified in creating the linear regression model using SAS Visual Statistics? a) interaction term b) group-by variable c) variable selection d) continuous effects 07. Refer to the exhibit: Which is the modeling approach that should be used when fitting the Target Gift Amount variable? a) Linear regression model with Interaction effects. b) Generalized linear model with a Poisson distribution and Identity link. c) Generalized linear model with a Normal distribution and Log Link. d) Logistic regression model. 08. In the below nonparametric logistic regression results display, where would you click to get a plot of significant continuous effects? Solution: Determine whether the given solution is correct?
a) Correct b) Incorrect 09. Which statement is TRUE regarding a generalized additive model (GAM) in SAS Visual Analytics? a) GAM assumes a strict linear relationship between the predictors and the response function. b) The roughness penalty controls the balance between goodness of fit and the roughness of the spline curve. c) Specification of a spline effect is optional. d) A larger maximum degrees of freedom for the univariate spline term enforces a less complex fit. 10. Which model does not produce score code? a) Decision Tree using interactive mode b) Regression using interaction effects c) Regression using the group by option d) Decision Tree using the rapid growth option Answers: Question: 01: Answer: a, d, e Question: 02: Answer: b Question: 03: Answer: c Question: 04: Answer: a Question: 05: Answer: c Question: 06: Answer: b Question: 07: Answer: c Question: 08: Answer: a Question: 09: Answer: b Question: 10: Answer: a How to Register for SAS Visual Modeling Certification Exam? Visit site for Register SAS Visual Modeling Certification Exam. 11/1/2021 0 Comments Get Quality Preparation with SAS Statistical Business Analyst (A00-240) CertificationSAS Statistical Business Analyst certification questions and exam summary helps you to get focused on the exam. This guide also helps you to be on A00-240 exam track to get certified with good score in the final exam. SAS Statistical Business Analyst (A00-240) Certification Summary
SAS Statistical Business Analyst (A00-240) Certification Exam Syllabus 01. ANOVA - 10% Verify the assumptions of ANOVA - Explain the central limit theorem and when it must be applied - Examine the distribution of continuous variables (histogram, box -whisker, Q-Q plots) - Describe the effect of skewness on the normal distribution - Define H0, H1, Type I/II error, statistical power, p-value - Describe the effect of sample size on p-value and power - Interpret the results of hypothesis testing - Interpret histograms and normal probability charts - Draw conclusions about your data from histogram, box-whisker, and Q-Q plots - Identify the kinds of problems may be present in the data: (biased sample, outliers, extreme values) - For a given experiment, verify that the observations are independent - For a given experiment, verify the errors are normally distributed - Use the UNIVARIATE procedure to examine residuals - For a given experiment, verify all groups have equal response variance - Use the HOVTEST option of MEANS statement in PROC GLM to asses response variance Analyze differences between population means using the GLM and TTEST procedures - Use the GLM Procedure to perform ANOVA CLASS statement MODEL statement MEANS statement OUTPUT statement - Evaluate the null hypothesis using the output of the GLM procedure - Interpret the statistical output of the GLM procedure (variance derived from MSE, F value, p-value R**2, Levene's test) - Interpret the graphical output of the GLM procedure - Use the TTEST Procedure to compare means Perform ANOVA post hoc test to evaluate treatment effect - Use the LSMEANS statement in the GLM or PLM procedure to perform pairwise comparisons - Use PDIFF option of LSMEANS statement - Use ADJUST option of the LSMEANS statement (TUKEY and DUNNETT) - Interpret diffograms to evaluate pairwise comparisons - Interpret control plots to evaluate pairwise comparisons - Compare/Contrast use of pairwise T-Tests, Tukey and Dunnett comparison methods Detect and analyze interactions between factors - Use the GLM procedure to produce reports that will help determine the significance of the interaction between factors. MODEL statement - LSMEANS with SLICE=option (Also using PROC PLM) - ODS SELECT - Interpret the output of the GLM procedure to identify interaction between factors: - p-value - F Value - R Squared - TYPE I SS - TYPE III SS 02. Linear Regression - 20% Fit a multiple linear regression model using the REG and GLM procedures - Use the REG procedure to fit a multiple linear regression model - Use the GLM procedure to fit a multiple linear regression model Analyze the output of the REG, PLM, and GLM procedures for multiple linear regression models - Interpret REG or GLM procedure output for a multiple linear regression model: convert models to algebraic expressions - Convert models to algebraic expressions - Identify missing degrees of freedom - Identify variance due to model/error, and total variance - Calculate a missing F value - Identify variable with largest impact to model - For output from two models, identify which model is better - Identify how much of the variation in the dependent variable is explained by the model - Conclusions that can be drawn from REG, GLM, or PLM output: (about H0, model quality, graphics) Use the REG or GLMSELECT procedure to perform model selection - Use the SELECTION option of the model statement in the GLMSELECT procedure - Compare the differentmodel selection methods (STEPWISE, FORWARD, BACKWARD) - Enable ODS graphics to display graphs from the REG or GLMSELECT procedure - Identify best models by examining the graphical output (fit criterion from the REG or GLMSELECT procedure) - Assign names to models in the REG procedure (multiple model statements) Assess the validity of a given regression model through the use of diagnostic and residual analysis - Explain the assumptions for linear regression - From a set of residuals plots, asses which assumption about the error terms has been violated - Use REG procedure MODEL statement options to identify influential observations (Student Residuals, Cook's D, DFFITS, DFBETAS) - Explain options for handling influential observations - Identify collinearity problems by examining REG procedure output - Use MODEL statement options to diagnose collinearity problems (VIF, COLLIN, COLLINOINT) 03. Logistic Regression - 25% Perform logistic regression with the LOGISTIC procedure - Identify experiments that require analysis via logistic regression - Identify logistic regression assumptions - logistic regression concepts (log odds, logit transformation, sigmoidal relationship between p and X) - Use the LOGISTIC procedure to fit a binary logistic regression model (MODEL and CLASS statements) Optimize model performance through input selection - Use the LOGISTIC procedure to fit a multiple logistic regression model - LOGISTIC procedure SELECTION=SCORE option - Perform Model Selection (STEPWISE, FORWARD, BACKWARD) within the LOGISTIC procedure Interpret the output of the LOGISTIC procedure - Interpret the output from the LOGISTIC procedure for binary logistic regression models: Model Convergence section - Testing Global Null Hypothesis table - Type 3 Analysis of Effects table - Analysis of Maximum Likelihood Estimates table - Association of Predicted Probabilities and Observed Responses Score new data sets using the LOGISTIC and PLM procedures - Use the SCORE statement in the PLM procedure to score new cases - Use the CODE statement in PROC LOGISTIC to score new data - Describe when you would use the SCORE statement vs the CODE statement in PROC LOGISTIC - Use the INMODEL/OUTMODEL options in PROC LOGISTIC - Explain how to score new data when you have developed a model from a biased sample 04. Prepare Inputs for Predictive Model Performance - 20% Identify the potential challenges when preparing input data for a model - Identify problems that missing values can cause in creating predictive models and scoring new data sets - Identify limitations of Complete Case Analysis - Explain problems caused by categorical variables with numerous levels - Discuss the problem of redundant variables - Discuss the problem of irrelevant and redundant variables - Discuss the non-linearities and the problems they create in predictive models - Discuss outliers and the problems they create in predictive models - Describe quasi-complete separation - Discuss the effect of interactions - Determine when it is necessary to oversample data Use the DATA step to manipulate data with loops, arrays, conditional statements and functions - Use ARRAYs to create missing indicators - Use ARRAYS, LOOP, IF, and explicit OUTPUT statements Improve the predictive power of categorical inputs - Reduce the number of levels of a categorical variable - Explain thresholding - Explain Greenacre's method - Cluster the levels of a categorical variable via Greenacre's method using the CLUSTER procedure METHOD=WARD option FREQ, VAR, ID statement Use of ODS output to create an output data set - Convert categorical variables to continuous using smooth weight of evidence Screen variables for irrelevance and non-linear association using the CORR procedure - Explain how Hoeffding's D and Spearman statistics can be used to find irrelevant variables and non-linear associations - Produce Spearman and Hoeffding's D statistic using the CORR procedure (VAR, WITH statement) - Interpret a scatter plot of Hoeffding's D and Spearman statistic to identify irrelevant variables and non-linear associations Screen variables for non-linearity using empirical logit plots - Use the RANK procedure to bin continuous input variables (GROUPS=, OUT= option; VAR, RANK statements) - Interpret RANK procedure output - Use the MEANS procedure to calculate the sum and means for the target cases and total events (NWAY option; CLASS, VAR, OUTPUT statements) - Create empirical logit plots with the SGPLOT procedure - Interpret empirical logit plots 05. Measure Model Performance - 25% Apply the principles of honest assessment to model performance measurement - Explain techniques to honestly assess classifier performance - Explain overfitting - Explain differences between validation and test data - Identify the impact of performing data preparation before data is split Assess classifier performance using the confusion matrix - Explain the confusion matrix - Define: Accuracy, Error Rate, Sensitivity, Specificity, PV+, PV- - Explain the effect of oversampling on the confusion matrix - Adjust the confusion matrix for oversampling Model selection and validation using training and validation data - Divide data into training and validation data sets using the SURVEYSELECT procedure - Discuss the subset selection methods available in PROC LOGISTIC - Discuss methods to determine interactions (forward selection, with bar and @ notation) - Create interaction plot with the results from PROC LOGISTIC - Select the model with fit statistics (BIC, AIC, KS, Brier score) Create and interpret graphs (ROC, lift, and gains charts) for model comparison and selection - Explain and interpret charts (ROC, Lift, Gains) - Create a ROC curve (OUTROC option of the SCORE statement in the LOGISTIC procedure) - Use the ROC and ROCCONTRAST statements to create an overlay plot of ROC curves for two or more models - Explain the concept of depth as it relates to the gains chart Establish effective decision cut-off values for scoring - Illustrate a decision rule that maximizes the expected profit - Explain the profit matrix and how to use it to estimate the profit per scored customer - Calculate decision cutoffs using Bayes rule, given a profit matrix - Determine optimum cutoff values from profit plots - Given a profit matrix, and model results, determine the model with the highest average profit SAS Statistical Business Analyst (A00-240) Certification Questions 01. Refer to the REG procedure output: What is the most important predictor of the response variable? a) intercept b) overhead c) scrap d) raining 02. An analyst builds a logistic regression model which is 75% accurate at predicting the event of interest on the training data set. The analyst presents this accuracy rate to upper management as a measure of model assessment.What is the problem with presenting this measure of accuracy for model assessment? a) This accuracy rate is redundant with the misclassification rate. b) It is pessimistically biased since it is calculated from the data set used to train the model. c) This accuracy rate is redundant with the average squared error. d) It is optimistically biased since it is calculated from the data used to train the model. 03. The LOGISTIC procedure will be used to perform a regression analysis on a data set with a total of 10,000 records. A single input variable contains 30% missing records.How many total records will be used by PROC LOGISTIC for the regression analysis?Note:- You can use calculator for this question a) 7000 b) 9000 c) 7009 d) 9007 04. Which statement is an assumption of logistic regression? a) The sample size is greater than 100. b) The logit is a linear function of the predictors. c) The predictor variables are not correlated. d) The errors are normally distributed. 05. An analyst is screening for irrelevant variables by estimating strength of association between each input and the target variable. The analyst is using Spearman correlation and Hoeffding's D statistics in the CORR procedure.What would likely cause some inputs to have a large Hoeffding and a near zero Spearman statistic? a) nonmonotonic association between the variables b) linear association between the variables c) monotonic association between the variables d) no association between the variables 06. Refer to the exhibit: For the ROC curve shown, what is the meaning of the area under the curve? a) percent concordant plus percent tied b) percent concordant plus (.5 * percent tied) c) percent concordant plus (.5 * percent discordant) d) percent discordant plus percent tied 07. When selecting variables or effects using SELECTION=BACKWARD in the LOGISTIC procedure, the business analyst's model selection terminated at Step 3.What happened between Step 1 and Step 2? a) DF increased. b) AIC increased. c) Pr > Chisq increased. d) - 2 Log L increased. 08. A financial analyst wants to know whether assets in portfolio A are more risky (have higher variance) than those in portfolio B. The analyst computes the annual returns (or percent changes) for assets within each of the two groups and obtains the following output from the GLM procedure: Which conclusion is supported by the output?
a) Assets in portfolio A are significantly more risky than assets in portfolio B. b) Assets in portfolio B are significantly more risky than assets in portfolio A. c) The portfolios differ significantly with respect to risk. d) The portfolios do not differ significantly with respect to risk. 09. An analyst has determined that there exists a significant effect due to region. The analyst needs to make pairwise comparisons of all eight regions and wants to control the experimentwise error rate.Which GLM procedure statement would provide the correct output? a) lsmeans Region / pdiff=all adjust=dunnett; b) lsmeans Region / pdiff=all adjust=tukey; c) lsmeans Region / pdiff=all adjust=lsd; d) lsmeans Region / pdiff=all adjust=none; 10. A linear model has the following characteristics:- a dependent variable (y)- one continuous predictor variables (x1) including a quadratic term (x12)- one categorical predictor variable (c1 with 3 levels)- one interaction term (c1 by x1)Which SAS program fits this model? a) proc glm data=SASUSER.MLR;class c1;model y = c1 x1 x1sq c1byx1 /solution;run; b) proc reg data=SASUSER.MLR;model y = c1 x1 x1sq c1byx1 /solution;run; c) proc glm data=SASUSER.MLR;class c1;model y = c1 x1 x1*x1 c1*x1 /solution;run; d) proc reg data=SASUSER.MLR;model y = c1 x1 x1*x1 c1*x1;run; Answers: Question: 01 - Answer: b Question: 02 - Answer: d Question: 03 - Answer: a Question: 04 - Answer: b Question: 05 - Answer: a Question: 06 - Answer: b Question: 07 - Answer: d Question: 08 - Answer: c Question: 09 - Answer: b Question: 10 - Answer: c How to Register for SAS Statistical Business Analyst Certification Exam? Visit site for Register SAS Statistical Business Analyst Certification Exam. |
|